According to Michael Thomas’ analysis, in 2023, Google and Microsoft will each consume 24 TWh of electricity, more than the consumption of over 100 countries, including Iceland, Ghana, and Tunisia. While the large amounts of energy used represent a significant environmental impact for these tech giants, it is important to note that Google and Microsoft also generate more revenue than many countries. Additionally, companies such as Intel, Google, and Microsoft are leading the adoption of renewable energy within their industries.
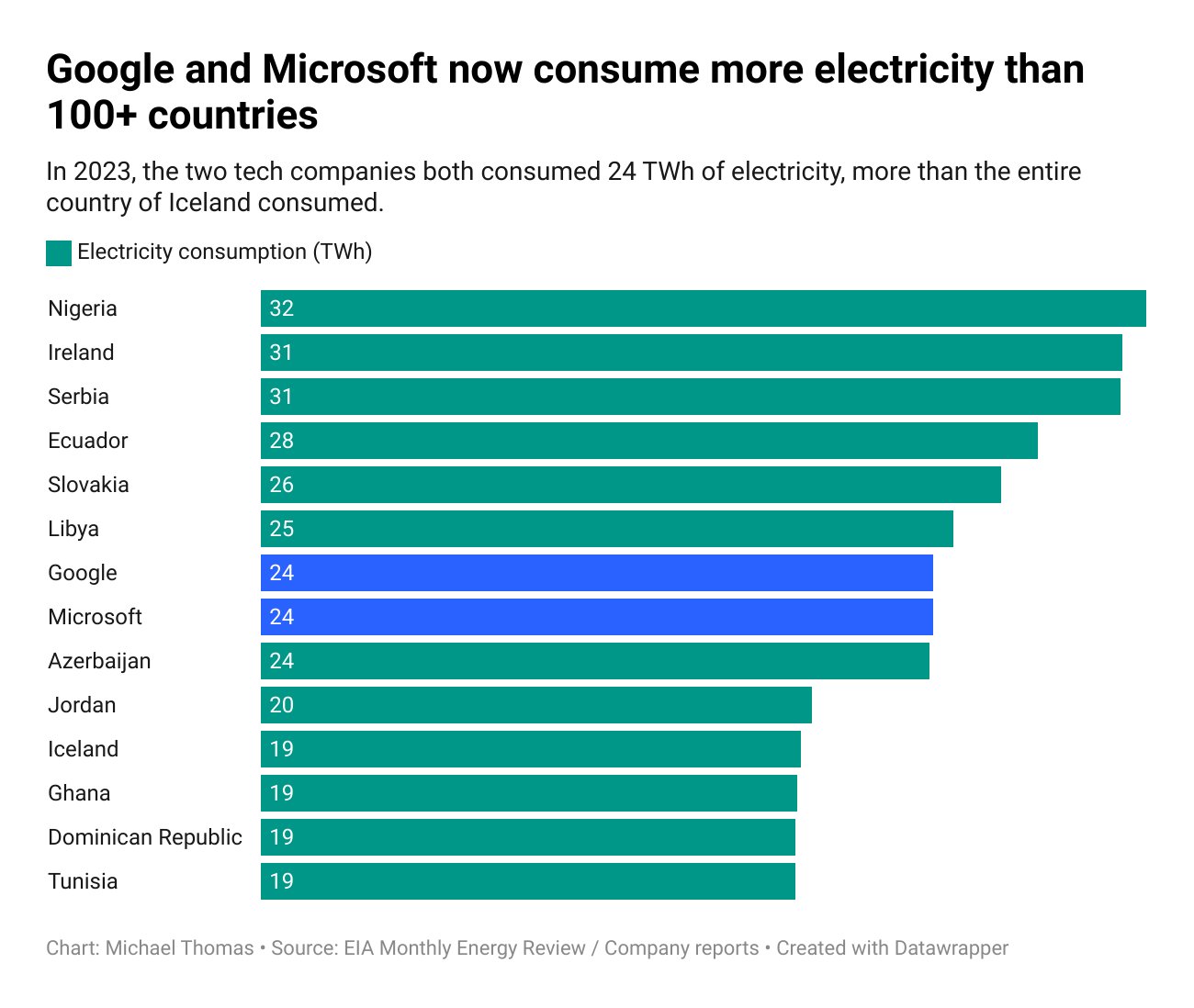
A detailed analysis reveals that Google and Microsoft’s electricity consumption (24 TWh in 2023) is comparable to that of Azerbaijan (population 10.14 million) and higher than that of several other countries. For example, Iceland, Ghana, Dominican Republic, and Tunisia consumed 19 TWh each, and Jordan consumed 20 TWh. Of course, there are countries that consume more electricity than Google and Microsoft. For example, Slovakia, with a population of 5.4 million, consumes 26 TWh.
This comparison highlights the enormous energy needs of tech companies. The data centers operated by Google and Microsoft have a significant environmental impact. But how do their electricity consumption and revenues compare to some of the countries mentioned above?
According to Google itself, in 2023, Google generated revenue of $305.6 billion, and its economic impact, which includes tools like Google Search, Google Cloud, and YouTube, contributed approximately $739 billion to the economy.
Microsoft has announced that it will have revenue of $211.9 billion in 2023. Considering that the majority of the world’s population uses Microsoft Windows and Microsoft Office, and that many online applications run on Microsoft Azure, the economic impact of Microsoft products is likely in the trillions of dollars.
Comparing this with countries with similar energy consumption, Azerbaijan’s GDP in 2023 will be approximately $78 billion, Slovakia’s GDP will be approximately $127 billion, and Iceland’s GDP will be approximately $30 billion.
The economic output of Google and Microsoft far exceeds the GDP of these countries, highlighting the massive financial scale of these tech giants relative to their massive electricity consumption.
The massive electricity consumption by Google and Microsoft highlights the need for a discussion on sustainability and renewable energy adoption within the tech industry, while these companies are leading the adoption of renewable energy sources in their industries.
In fact, Google has been a pioneer in the use of renewable energy for many years: The company has been carbon neutral since 2007, and aims to run all of its data centers on carbon-free energy 24/7 by 2030. In 2023, Google announced continued investments in renewable energy projects, expanding its portfolio to include a variety of wind, solar, and other renewable energy sources.
Microsoft has committed to being carbon negative by 2030, meaning it aims to remove more carbon from the environment than it emits. The company also aims to have zero waste production and positive water use by the same year. In 2023, Microsoft will increase its contracted portfolio of renewable energy assets to more than 19.8 gigawatts, covering projects in 21 countries. The company is also working to reduce its direct operational emissions and indirect emissions, especially those related to the construction of new data centers and hardware components.

